You might have come across advertisements promoting peptides in skincare products and different supplements, sparking curiosity: What exactly are peptides? Do they merit your interest, and might they have an impact on your health?
Indeed, peptides are worth delving into. Continue reading to discover how peptides could potentially aid in diminishing overall inflammation, decelerating the aging process, and contributing to various aspects of your health.
What Are Peptides?
Peptides are similar to proteins, comprising strings of amino acids. However, they tend to be smaller, sometimes composed of just two amino acids, making them readily absorbable by the body, whether through the digestive system or the skin.
Your body naturally produces peptides as part of its regular functioning; these are referred to as endogenous peptides. For instance, insulin, consisting of 51 amino acids, is an endogenous peptide.
Peptides are found in various foods such as meats, soy, milk, oats, wheat, and eggs, termed exogenous peptides. Additionally, scientists can synthesize peptides in laboratories. Insulin serves as a prime example of this synthetic process, being the first peptide ever created in a lab.
The effects of different peptides on the body vary, largely contingent upon the types of amino acids they contain. They play crucial roles in numerous bodily processes, spanning from digestion to wound healing to cellular communication.
Exogenous peptides generally carry fewer side effects than numerous medications, given their natural compatibility with the body and breakdown into natural amino acids. Additionally, their smooth passage through the body streamlines processing for enhanced efficiency.
Peptides vs. Proteins
When you encounter the term “amino acids,” your mind likely jumps straight to proteins — and you’re absolutely correct. Proteins are indeed chains of amino acids. So, what sets proteins apart from peptides?
The distinction lies in the length of the amino acid chain involved. Peptides consist of shorter chains of amino acids, whereas proteins comprise longer chains. Typically, scientists classify a chain of 20 or fewer amino acids as a peptide.
The abbreviated length of peptides enables them to seamlessly navigate through skin layers, cell membranes, and the gastrointestinal tract. This allows them to swiftly and effortlessly access the bloodstream and target specific areas of the body as required. This attribute proves advantageous for scientists producing exogenous peptides, as their shorter length simplifies the synthesis and manufacturing process.
Types of Peptides
Peptides are categorized by scientists based on their distinct properties and functions. Among the most prevalent types of peptides are:
- Anticancer peptides: These compact peptides combat cancer cells by puncturing holes in their membranes, a mechanism utilized in cancer treatment by researchers.
- Antifungal peptides: These peptides safeguard the body against fungal infections and diseases caused by fungi, including molds.
- Antimicrobial peptides: Endogenous peptides crucial to the immune response, aiding in the body’s defense against invasive and harmful organisms.
- Bacterial peptides: Produced by bacteria within the body, these peptides encompass lipoproteins and certain enzymes.
- Cardiovascular peptides: These peptides contribute to regulating blood pressure and combating conditions such as congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and atherosclerosis.
- Endocrine peptides: These specialized peptides play a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of your endocrine system. They enhance insulin sensitivity, boost metabolism, regulate appetite and weight, combat inflammation, regulate bone growth, and manage the sleep/wakefulness cycle. Additionally, they assist in controlling thyroid and sex hormones.
- Neuropeptides: Originating from your neurons, these peptides operate within your nervous system and brain. They encompass familiar neurotransmitters such as epinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
- Opioid peptides: Working in conjunction with your hypothalamus and pituitary gland, these peptides help modulate stress and pain responses.
- Plant peptides: These exogenous peptides, obtained from plants through ingestion, play vital roles in regulating cholesterol and blood pressure. Furthermore, they offer protection against inflammation, cancer, microbial infections, and oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
Scientists utilize a range of synthesis techniques to develop peptides aimed at enhancing health in multifaceted ways. For example, synthesized creatine peptides are renowned for their capacity to fortify muscle strength, while artificial collagen peptides have demonstrated remarkable advantages for promoting skin health.
How Can Peptides Benefit Your Health?
Peptides, whether occurring naturally within your body or engineered in a laboratory setting, have the potential to significantly enhance your overall health and well-being.
Enhanced Healing Abilities
Peptides serve as integral components in the healing process through diverse mechanisms. Collagen, for instance, stands out as a pivotal peptide that facilitates wound healing and maintains skin vitality. Additionally, specific antimicrobial peptides exhibit potential in addressing various skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis, contributing to their healing. Furthermore, an array of bioactive peptides function as antioxidants, augmenting the healing process by mitigating inflammation.
Delaying the Aging Process
An assortment of peptides contribute to the deceleration of aging through diverse mechanisms. Peptides administered topically to the skin demonstrate potential in shielding against sun damage and enhancing blood circulation, thereby promoting skin elasticity and reducing the formation of wrinkles. Moreover, internally, peptides such as collagen aid in maintaining the flexibility and strength of muscles, ligaments, and tendons, fostering a sense of youthfulness from within.
Prevention of Bone Loss
Research indicates that consuming peptides could potentially mitigate age-related bone loss, a common concern among aging individuals. Peptides have been shown to enhance bone mineral density, and certain peptide-based medications have
received government approval for treating osteoporosis received FDA approval for treating osteoporosis.
Muscle Mass Enhancement
Specific peptides, such as human growth hormone peptides, have been found to effectively promote muscle mass development, particularly when combined with resistance training. Additionally, they aid in muscle repair post-exertion and enhance joint flexibility. However, it’s crucial to note that not all over-the-counter supplements claiming to build muscle are safe for consumption. Certain supplements containing peptides, or purportedly containing them, may lead to adverse effects, such as elevated blood sugar levels. Hence, it is imperative to consult with healthcare professionals before contemplating peptide supplementation.
Enhanced Skin and Hair Health
Certain naturally occurring antimicrobial peptides produced by your body play a vital role in maintaining skin health, safeguarding against wounds and bacterial damage. Supplementing with exogenous versions of these peptides can offer protection against skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and acne. Typically, these external peptide formulations contain collagen, renowned for its capacity to enhance skin elasticity and moisture retention, while also promoting thicker and healthier hair. It’s widely acknowledged that collagen levels naturally decline with age, underscoring the potential necessity for peptide therapy to preserve skin and hair health as you age.
Increased Testosterone Levels
Certain peptides have been shown to stimulate the production and release of hormones associated with testosterone production. By incorporating these peptides into your regimen, you can naturally enhance your body’s testosterone levels without resorting to supplemental testosterone intake.
Enhancements in Brain Function
Opiate peptides offer a spectrum of advantages, including alleviating anxiety, depression, and stress, along with providing pain relief. Ongoing research aims to elucidate the potential benefits of exogenous peptide variants, which bind to specific brain receptors, in enhancing brain function and mitigating stress through medical intervention.
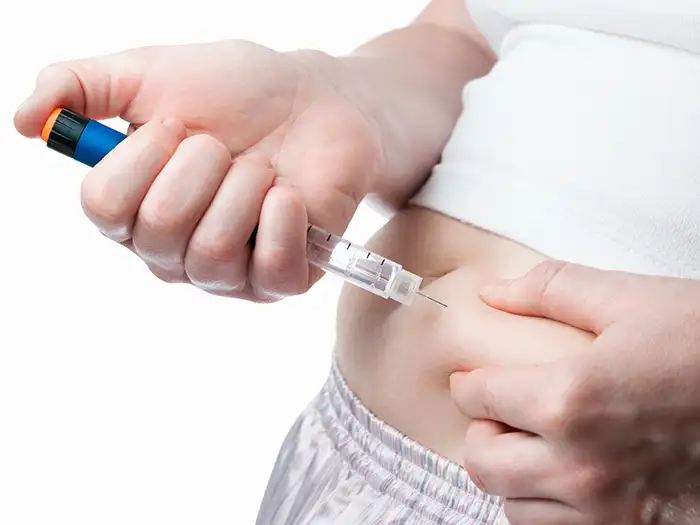
Peptide Therapy
Through peptide therapy, healthcare professionals can utilize peptides to enhance various bodily functions, offering benefits to bones, muscles, skin, brain function, and other organs. Peptide therapy encompasses diverse delivery methods tailored to the specific peptides and desired outcomes. Some peptides are administered via injections, while others are formulated for absorption through the skin, either via topical creams or transdermal patches. Additionally, peptide treatment options may include oral or dietary supplements, as well as nasal sprays. Notably, the FDA has approved over Over 80 types of peptide-based medications have been officially approved, addressing a wide range of conditions spanning
from diabetes and osteoporosis to HIV and testosterone deficiency.
Side Effects of Peptide Usage
Due to their natural occurrence in the human body, peptides typically entail minimal side effects. Even exogenous peptides, found in food, generally pose no adverse reactions. In certain instances, exogenous peptides are metabolized into individual amino acids before entering the bloodstream.
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should exercise caution and consult their doctor before considering peptide therapy. Additionally, individuals taking specific medications or managing certain chronic conditions should seek medical advice prior to peptide therapy initiation. While adverse effects are uncommon, allergic reactions to certain peptides may occur, manifesting as hives, swelling, heart palpitations, breathing difficulties, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, or dizziness. Individuals with skin sensitivities might also experience itching or rashes upon using topical creams containing peptides. Should any adverse reactions arise, it is advisable to promptly consult the prescribing physician.
The Future of Peptides
Research in the medical applications of peptides is advancing rapidly. As novel peptide formulations demonstrate their effectiveness in slowing the aging process, enhancing muscle growth, and safeguarding against various forms of damage, one can anticipate the emergence of new therapeutic uses for these versatile chains of amino acids in the foreseeable future.
Nevertheless, much of the ongoing research remains at the cutting edge. Thus, it is essential to collaborate with healthcare professionals when exploring the potential advantages and benefits of peptide therapy for one’s own health. Your doctor is uniquely positioned to discuss the potential benefits, suitability of specific peptide therapy for your individual circumstances, and any associated risks. Relying on random supplements purchased over the counter or online is unwise, particularly when experimenting with relatively new medical treatments.
What Could Peptides Mean for You?
Continual exploration of peptides for novel therapeutic applications is underway, aiming to unlock their full potential as valuable medications. Over the past three decades, research into peptides has surged by more than 1,300%, with ongoing advancements on the horizon.
We are dedicated to remaining at the forefront of the latest advancements in peptide research, stemming from our desire to assist you in pursuing and attaining optimal health. Whether it involves remarkable breakthroughs in anti-aging therapy facilitated by HGH (human growth hormone) peptides or other hormonally based treatments, we are here to support you on your path to wellness. Reach out to us today to have all your inquiries regarding peptides addressed and to discover how this groundbreaking therapy can truly transform your life.